Matplotlib 是一个Python 2D绘图库,它可以在各种平台上以各种硬拷贝格式和交互式环境生成出具有出版品质的图形。 Matplotlib可用于Python脚本,Python和IPython shell,Jupyter笔记本,Web应用程序服务器和四个图形用户界面工具包
Pyplot
matplotlib.pyplot是matplotlib的基于状态的接口。它提供了类似MATLAB的绘图方式。
import matploblib.pyplot as plt |
Workflow
- Step 1 Prepare data
- Step 2 Create figure
- Step 3 Add axes
- Step 4 Customize plot
- Step 5 Save plot
- Step 6 Show plot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
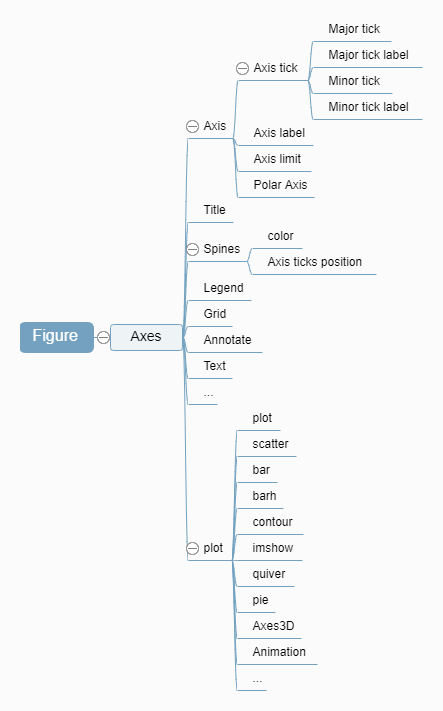
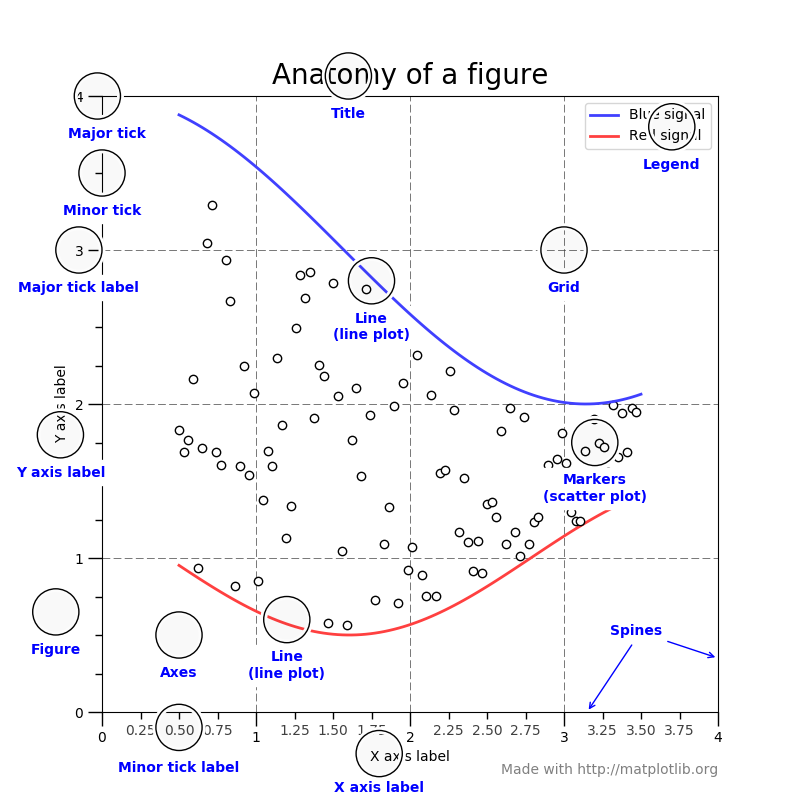
Figure and Axes
一般通过get_<part>方法获得组件属性,set_<part>方法重设组件。
Create Figure
plt.figure(num=None, figsize=None, dpi=None, facecolor=None, edgecolor,...)
Parameters:
num : (integer or string) figure编号
figsize : (tuple of integers) figure尺寸
dpi : (integer) 分辨率
Add Axes
fig.add_subplot(nrows, ncols, plot_number)
fig=plt.figure() |
nrows, ncols, plot_number: 分割figure行数和列数,axes的位置
fig.add_axes(rect) 可以添加图中图
Parameters:
rect : [left, bottom, width, height]
projection : [‘aitoff’ | ‘hammer’ | ‘lambert’ | ‘mollweide’ | ‘polar’ | ‘rectilinear’], optional
polar : boolean, optional
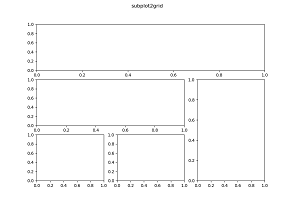
plt.subplot2grid(shape, loc, rowspan=1, colspan=1) 建造不规则axes
Parameters:
shape: figue分割
loc: 原点位置,基于shape分割结果
rowspan, colspan: 行或列的跨度
ax1 = plt.subplot2grid((3,3), (0,0), colspan=3) |
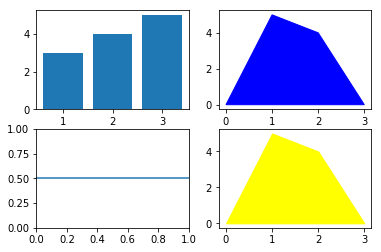
plt.subplots
plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, sharex=False, sharey=False,...) Create a figure and a set of subplots
Parameters:
nrows, ncols : (int) 分割figure行数和列数
sharex, sharey : bool or {‘none’, ‘all’, ‘row’, ‘col’}, 是否共享坐标轴
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2,2) |
Plot
| 常用图形 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| plot(x,y,data) | 默认折线图 |
| scatter(x, y, s, c, marker, cmap) | 散点图{s:size,c:color} |
| hist(x, bins) | 直方图 |
| bar(x, height, width, fill) | 柱状图 |
| barh(y, height, width, fill) | 横向柱状图 |
| boxplot(y) | 箱线图 |
| violinplot(y) | 小提琴 |
| axhline(y) | 水平线 |
| axvline(x) | 垂直线 |
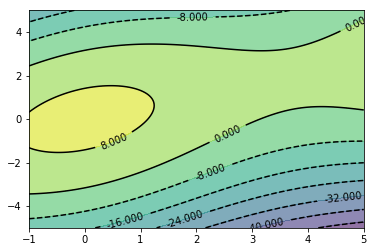
| contourf(X,Y,Z,N,cmap) | 等高线填充 |
| contour(X,Y,Z,N) | 等高线线条 |
| imshow() | 热图 |
| quiver() | 2D箭头场 |
| streamplot() | 2D矢量场 |
| pie(x, explode, labels, colors) | 饼图 |
| acorr(x) | 自相关 |
| fill(x,y) | 填充多边形 |
| fill_between(x,y) | 两曲线间填充 |
Parameters:
Alpha
Colors©, Color Bars & Color Maps(cmap)
Markers: marker , size
Line: linestyle(ls), linewidth
x=[0,1,2,3] |
import numpy as np |
Parts of Axes
| Axis(x axis) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ax.set_xlabel(xlabel, fontdict=None, labelpad=None) | x轴标签 |
| ax.set_xticks(ticks, minor=False) | x轴刻度 |
| ax.set_xticklabels(labels, fontdict=None, minor=False) | x轴刻度标签 |
| ax.set_xlim(left=None, right=None) | x轴限制 |
| ax.axis(‘scaled’) | xy轴标准 |
| ax.set_title(label, fontdict=None, loc=‘center’) | loc : {‘center’, ‘left’, ‘right’}, str, optional |
# x轴刻度标签属性设置,其他组件属性设置基本相同 |
Spines
ax.spines['left'].set_color('b') # 左侧线条修改为蓝色 |
spines: {left,right,top,bottom}
Legend
ax.legend(loc='best', handles,labels)
handles:图例控制对象
labels:图例标签
loc: string or 0:10
Grid
ax.grid(b=None, which='major', axis='both')
Parameters:
which: ‘major’ (default), ‘minor’, or ‘both’
axis: ‘both’ (default), ‘x’, or ‘y’
annotate and Text
ax.annotate()
Parameters:
s : str
xy : iterable
xytext : iterable, optional
xycoords : str, Artist, Transform, callable or tuple, optional
textcoords : str,Artist,Transform, callable or tuple, optional
fontsize:
arrowprops : dict, optional
ax.text(x, y, s, fontdict=None, withdash=False)
Save and Show
fig.savefig(fname) # or plt.savefig |
example
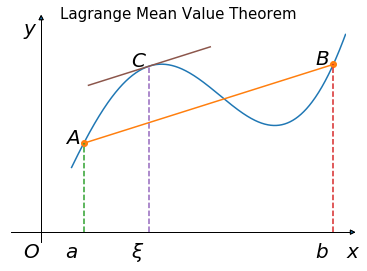
# ---------------------拉格朗日中值定理 |
Patches
from matplotlib import patches #图块 |
| 部分类 | 图形 |
|---|---|
| Arc | 弧度 |
| Arrow | 箭头 |
| Circle | 圆 |
| CirclePolygon | 多边形近似 |
| Ellipse | 椭圆 |
| Polygon | 多边形 |
| Rectangle | 矩形 |
| RegularPolygon | 正多边形 |
| Shadow | 阴影 |
Path
from matplotlib.path import Path |
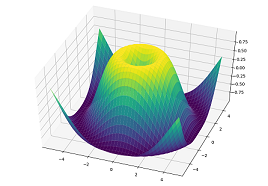
Axes3D
from matplotlib import cm |
Animation
import matplotlib.animation as animation |